Like most engineers out there, we try to focus as much as possible on automation. One of those ways is using modules when working with Terraform.
But sometimes, finding an efficient way to release and distribute those can present a challenge.
Therefore after some time of experimenting, I have a solution that might come in handy for those of you working with Github & Terraform.
Our focus will be set around Github Actions, and If you have not yet heard of them, then I recommend you check out the following link https://github.com/features/actions
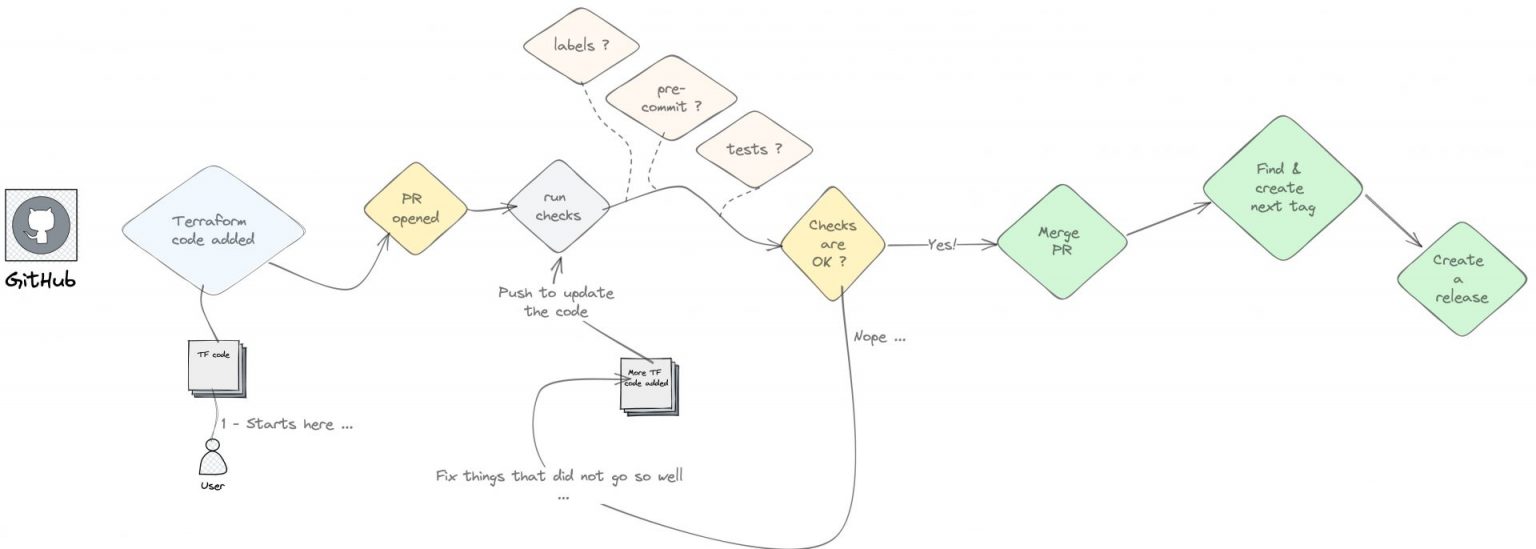
The flow we will be implementing today can be shows from high level overview as follow:
While working with Terraform modules it became apparent that after committing the code, it usually boiled down to several actions that needed to be executed for a complete modification of a Terraform module. Those actions were:
-
- Running terraform checks ( before merging a PR )
-
- updating the documentation
-
- finding out next semver for the module
-
- tagging the module ( or creating a release )
Based on those, our Raftech engineers created Github Actions workflows that use several actions to automate the above. This of course is only one way of many out there that support achieving this goal.
Checks
For every PR action, we run a set of checks. In our case, we decided we need to make sure base modules files are present, labels for semver are added, labels defining the purpose of the PR, and lastly that the code goes through pre-commit validations
Our resulting workflow in Github has the following content:
name: ci-checks-tf
on:
pull_request:
types: [opened, reopened, synchronize, labeled, unlabeled]
permissions:
id-token: write
contents: write
pull-requests: write
jobs:
pre-commit:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
container: ghcr.io/antonbabenko/pre-commit-terraform:v1.79.1
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v3
- name: 'pre-commit::add-github-repo-safe'
run: |
git config --global --add safe.directory $GITHUB_WORKSPACE
- name: 'pre-commit::run-all-checks'
run: |
pre-commit run -a --show-diff-on-failure -v
module-required-files:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v3
- name: 'tf-module::check-required-files'
id: check_files
uses: andstor/file-existence-action@v2
with:
files: "variables.tf, main.tf, README.md, versions.tf"
fail: true
label-required-semver:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: 'pr::check-required-semver'
uses: docker://agilepathway/pull-request-label-checker:latest
with:
prefix_mode: true
one_of: "release/" # patch , minor , major
repo_token: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
label-required-pr-type:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: 'pr::check-required-pr-type'
uses: docker://agilepathway/pull-request-label-checker:latest
with:
any_of: bug,enhancement,documentation,security
repo_token: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
label-do-not-merge:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: 'pr::check-required-semver'
uses: docker://agilepathway/pull-request-label-checker:latest
with:
none_of: do-not-merge
repo_token: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
To make sure these checks are mandatory – we set them up as required in the branch protection rules against the main/master branch.
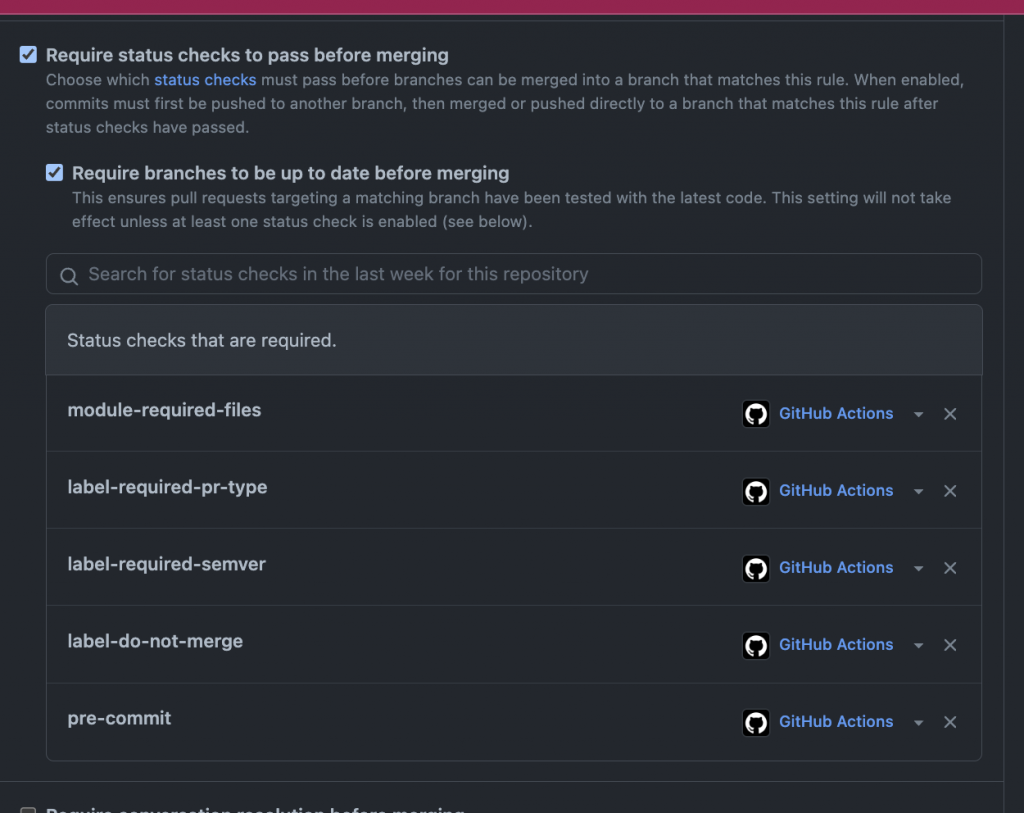
With these checks being required you will have on every PR in your modules repositories the checks doing the work of making sure your baseline for delivering of terraform modules are followed
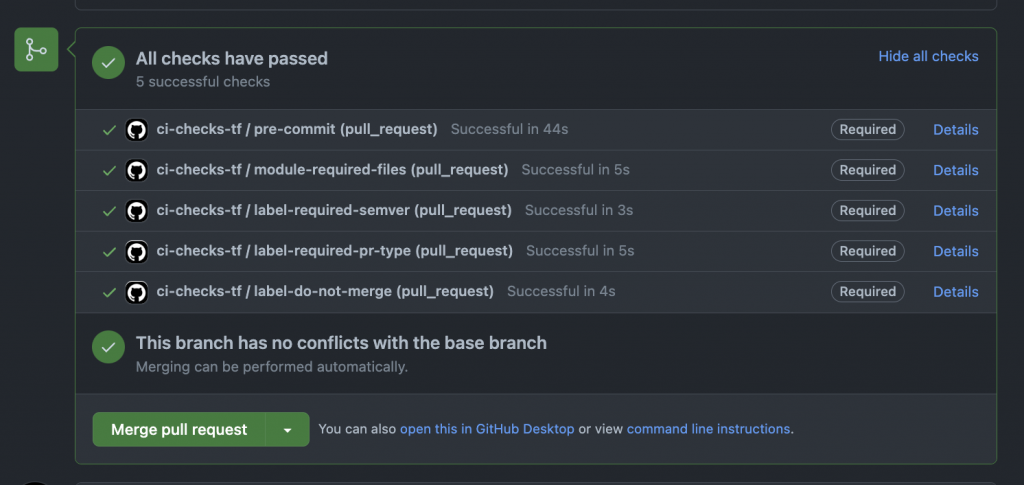
Release a new version
Once all of our checks have passed and our code is up to our requirements, we can create a new release. Of course, we want to have it done in a completely automated way – therefore we added one more action which will act upon a closed PR event. It will then automatically find the release label we use ( release/patch ; release/minor or release/major ) and use that information to bump our semver tag.
Once that is completed it will go ahead and create the final item – release.
name: v1-func-create-tag-and-release
on:
pull_request:
types: [closed]
jobs:
create-new-release:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v3
- uses: actions-ecosystem/action-release-label@v1
id: release-label
if: ${{ github.event.pull_request.merged == true }}
- uses: actions-ecosystem/action-get-latest-tag@v1
id: get-latest-tag
if: ${{ steps.release-label.outputs.level != null }}
- uses: actions-ecosystem/action-bump-semver@v1
id: bump-semver
if: ${{ steps.release-label.outputs.level != null }}
with:
current_version: ${{ steps.get-latest-tag.outputs.tag }}
level: ${{ steps.release-label.outputs.level }}
- uses: actions-ecosystem/action-push-tag@v1
if: ${{ steps.release-label.outputs.level != null }}
with:
tag: ${{ steps.bump-semver.outputs.new_version }}
message: '${{ steps.bump-semver.outputs.new_version }}: PR #${{ github.event.pull_request.number }} ${{ github.event.pull_request.title }}'
- name: 'gh::release'
if: ${{ steps.release-label.outputs.level != null }}
uses: softprops/action-gh-release@v1
with:
tag_name: ${{ steps.bump-semver.outputs.new_version }}
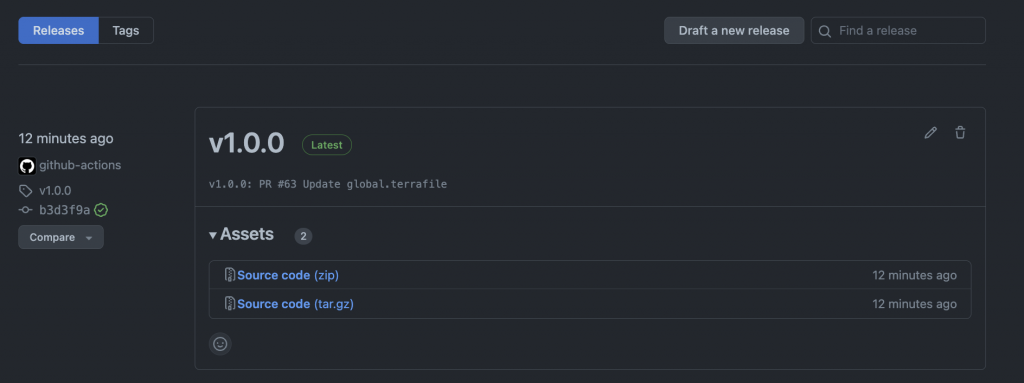
Once the last step is completed you will see the release on the repository page
Summary
Once the action completes its run you have made sure your code runs through your checks , have been tagged and a release have been created! At Raftech we believe that is the way you want to do your job 🙂 automated !